When Should I Consider Digital Advertising?
Having an established online presence and brand identity increases the effectiveness of your ad campaigns.
For this reason, it’s often a good idea to hold off on your first digital advertising campaign until your online presence is firmly established.
Reasons to Choose Digital Advertising
- Speed: It’s a fast mechanism for acquiring customers
- Scale: It’s a good way to scale up your presence
- Accessibility: Almost any business can benefit from digital ads
- Technology: Innovations like AI are expanding limits and possibilities
Digital Advertising Success Factors
- An established business
- Memorable branding
- A strong online presence
- A compelling entry offer
- High customer lifetime value
Unfortunately, a low barrier to entry has resulted in crowding in the digital ad space..
Thousands of “get-rich-quick” style business courses have emerged, almost all of them teaching some form of digital advertising.
Over the past several years, many business owners have had their patience exhausted by these first-time digital marketing entrepreneurs. That said, experienced digital advertising professionals have a high success rate when it comes to delivering an ROI to business owners.
If you can avoid all the amateurs, the benefit of hiring an experienced agency to run your ad campaign far outweighs the costs.
Digital Ads: Some Important Terms
Ad Creative
The image or video associated with your ad
Ad Copy
The written component of your ad
Ad Impression
When your ad is viewed
Conversion
The creation of a lead or a sale from an ad campaign
Conversion rate
The percentage of prospects that convert to a lead or sale
Click-through-rate (CTR)
The percentage of prospects that click an ad they see
Cost-per-click (CPC)
The cost of every click on an ad
Cost-per-“mile” (CPM)
The cost of 1000 ad impressions
Cost-per-conversion
The cost of a lead or sale
Direct-Response Marketing
Modern Digital Advertising… is an evolution of classical direct-response marketing…
Direct response marketing is a highly analytical and cost-controlled form of advertising. Most of the traditional advertising you’re familiar with from TV and Billboards is known as “mass-media” advertising. This is where corporations utilize their large marketing budgets to build widespread awareness.
In comparison, direct-response marketing is far more surgical: The marketer tests and tweaks every ad-variable before scaling the campaign.
Here are some questions direct-response marketers ask when building ad-campaigns:
- What images, colors and fonts are getting the most attention?
- What headlines and sub-headlines are getting the most attention?
- What “call-to-action” does the prospect find most compelling?
- At what point in the ad-copy/funnel are people dropping off?
- What price-point, offer, packaging, and/or guarantee provide the highest ROI?
The classical form of direct-response marketing was known as “direct-mail.”
Direct mail marketing is when marketer’s used postage marked letter-mail to sell their products and services. Direct-mail is orders of magnitude more difficult than digital advertising: Printing physical mail and buying postage is costly, sending mail is labour intensive, good data is scarce, and tracking is limited. Direct-mail marketers have only one tool in their toolbox to compensate for all these difficulties: create compelling advertising. And so they did. This is probably why many of history’s marketing greats – Claude Hopkins, David Ogilvy, Dan Kennedy, Gary Halbert – were all direct-mail marketers.
All we know about direct response marketing comes from the era of direct-mail era…
These advertising principles are based on unchanging principles of human psychology, so technology can’t change them.
The digital age has only accelerated the usefulness of these principles by making them easier and cheaper to apply.
The Lessons of Direct Mail Marketing
- Advertising is just salesmanship in print.
- An objective test is worth 1000 subjective opinions.
- Ads require a headline, sub-headline, and call-to-action
- Good advertising build’s curiosity and self-interest
- Ad-copy must be compelling, concise, and informal.
- Advertising requires a specific, well-researched customer avatar.
- Ads need a hook or angle that appeals to the target audience.

Search Advertising / PPC
You will hear many referring to search advertising as “pay-per-click” (PPC) advertising. This is because you only pay for an ad when a user clicks it. This can be compared to Facebook advertising, for example, where you pay per “impression” (every time someone views your ad).
Search advertising is a popular form of digital advertising for small-medium businesses. And it accounts for nearly 30-40% of total online advertising spend in the US and Canada.
With search advertising, your ads are shown to those already seeking your services. Since your prospects are already moving in your direction, this is the advertising equivalent of fishing by holding a net in a stream and taking whatever swims in.
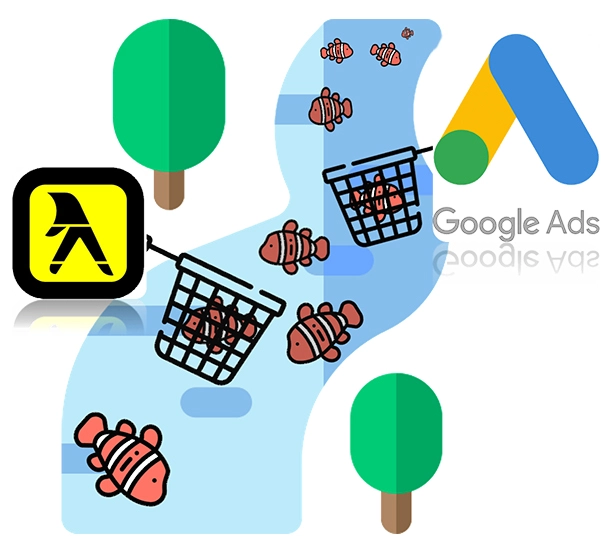
Search Ad Platforms
Good Search Ads:
The “Yellow Pages” of the modern era. Formerly known as “Adwords,” the Google ads platform accounts for 70%-80% of the entire search advertising market.
Microsoft Search Ads:
Although far less prominent than Google, this platform is not to be disregarded. The Microsoft advertising network includes practically every non-Google search engine like Bing, Yahoo, and DuckDuckGo. Surprisingly, the platform accounts for around 35% of the desktop search market in the US and Canada.
Waze:
A blend between local and search advertising, this platform is great for businesses with a physical presence.
Kijiji:
This platform is great for home-based businesses wanting to advertise local services.
Search Ad Pros and Cons
Relatively formulaic:
You won’t see much performance variation amongst competent search ad campaigns in the same location and niche.
Pay-Per-Click:
A user must click on your ad for you to be charged.
Low Volatility:
For the most part, different niches and different locations are all separate pockets of ad inventory. So your ad costs are likely to remain steady over time.
Limited supply:
There are only so many people searching each day for your services and there is no way to increase this volume.
Higher costs:
Naturally, with predictability and limited supply, comes an increased ad cost. The best way to manage the increased ad-cost is to find ways to maximize your customer lifetime value.
Elements of a Successful Search/PPC Campaign
Elements of a Successful Search/PPC Campaign
You will be bidding against other advertisers for your chosen keywords. Luckily, if you are a local business, you will only be bidding against other businesses in your area.
Cost-per-click increases with keyword competitiveness and geographic competitiveness.
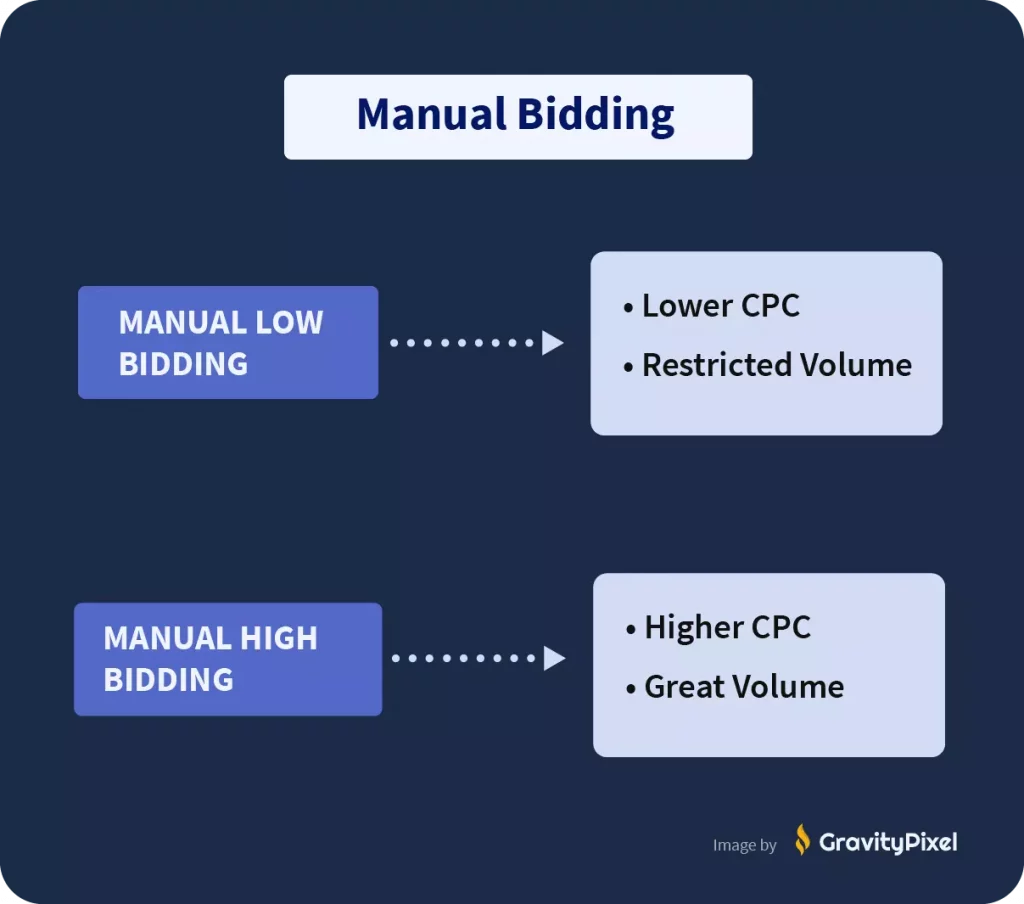
You can manually set a maximum bid, or you can set-up automated bidding and let search engines optimize your bidding for you. There are pros and cons to both strategies.
Generally speaking, setting a low manual bid will lower your cost per click, and therefore your customer acquisition costs. However, it will also restrict your volume.
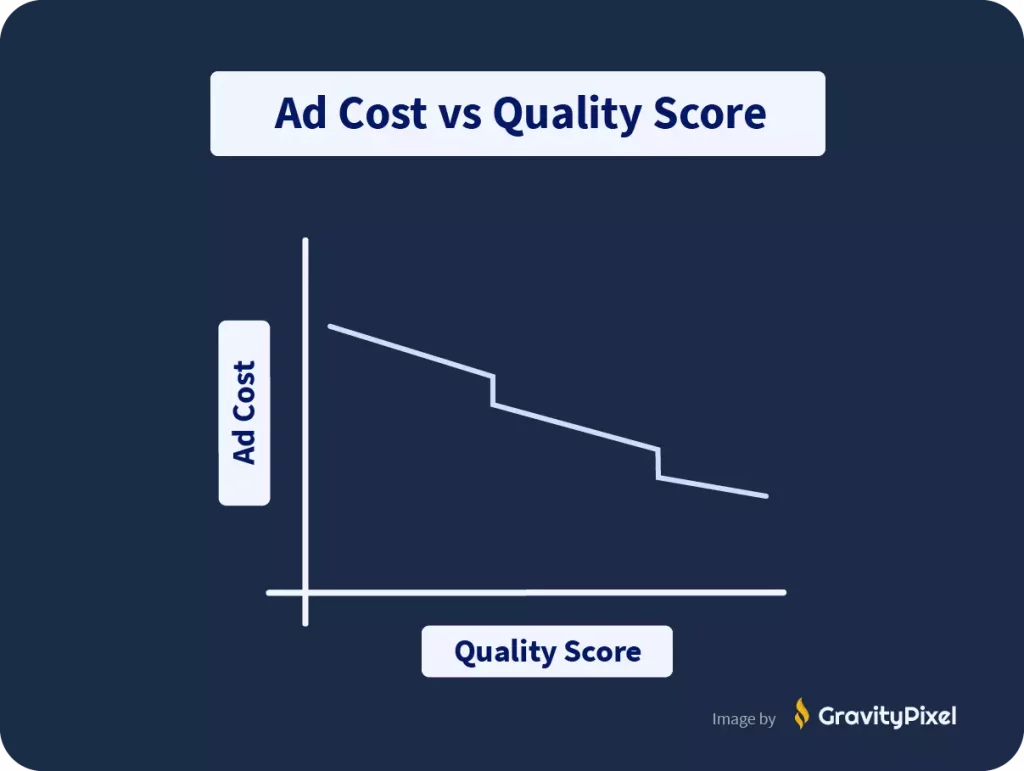
High “Quality Score”
Your bid isn’t the only factor that determines your place in the ad auction: Your ad is also given a quality score.
Your overall “ad-rank” is determined by your maximum bid multiplied by your quality score.
Put simply, advertisers with high-quality ads pay less: A high quality score can save you up to 50% on your ad costs while a low-quality score can inflate your ad costs by up to 400%. This is one reason why hiring a digital marketing agency for your PPC/search ad campaigns is a good idea: an optimized quality score will pay for itself on its own.
Efficient Keyword Selection
“Keywords” are the terms searchers use to find your services. The hallmark of search advertising is the placement of your ad against your chosen set of keywords.
It’s critical to ensure you are bidding on the right keywords, but you must also create a good list of “negative keywords:” these are keywords that you explicitly tell Google NOT to bid on.
For example, if you’re selling locksmith services, you want to bid on keywords like “locksmith near me.” But wouldn’t want to bid on keywords like “locksmith jobs” because those searchers, while using similar keywords, probably aren’t looking to purchase your services, they are looking to provide them.
A good list of negative keywords will prevent Google from draining your budget on clicks that have no chance of converting into customers.
When setting up a PPC ad-campaign, the Gravity Pixel Ads Team uses a proprietary keyword research workflow we call “The Intent array™.”
Setting up your Intent Array involves utilizing a suite of keyword research tools to collect hundreds, or even thousands, of relevant keywords. We then individually categorize each keyword according to a 10 point system. Finally, we add the “cream of the crop” keywords to your campaign, keywords we think should be tested, as well as the negative keywords.
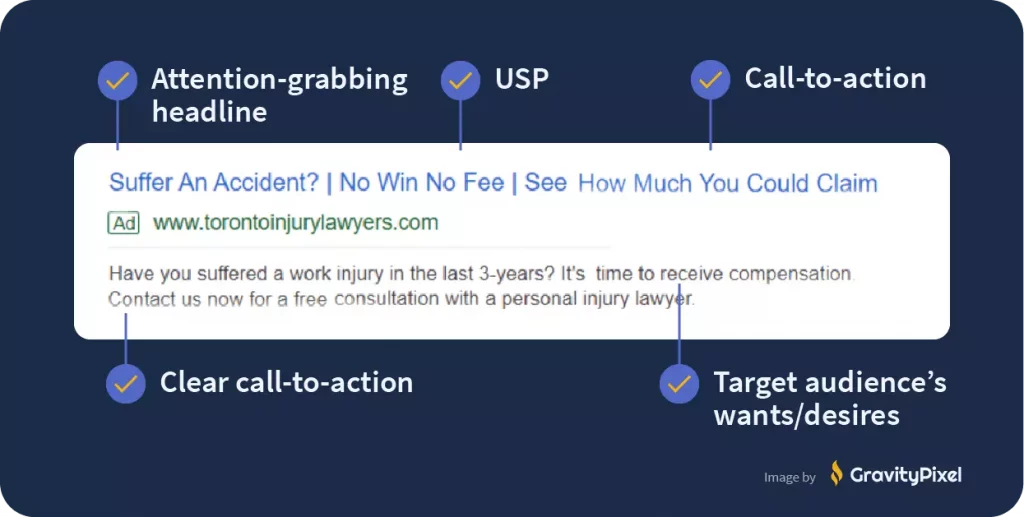
Compelling Ad Copy
Compared to other forms of digital advertising, search ads provide little room for marketing creativity:
There isn’t much space for ad copy, and there’s no place for pictures and/or video.
That said, there is a list of core fundamentals for optimizing search ads. Shockingly, many advertisers don’t even adhere to these marketing basics.
Optimized “Post-Click” Experience
The “post-click” experience refers to whatever takes place after a prospect clicks your ad. This will either be your website or a purpose built landing page.
The post-click experience must be optimized to maximize your ROI. Your aim should be that an above-average proportion of visitors become leads and/or customers.
To this end, it’s most important to optimize the following:
- Headlines
- Sales copy
- Page layout / clarity
- Lead magnet / CTA
A good post-click experience also improves your “quality score” by decreasing your “bounce rate.” The bounce rate refers to the number of visitors that leave the page before viewing its contents. Slow page speed is the main thing that increases bounce rate. But a poor “ad-scent” can also increase bounce rate. This is a lesser known concept that marketers often miss.
Ad-scent refers to the sense of validation a visitor gets upon immediately viewing your page that they are about to receive whatever they clicked for. To test your page’s ad-scent, you can perform something known as the “squint test:” This is where you ask a friend to squint their eyes before showing them your landing page. They are to then explain what your page is about. Whatever people guess your page is about while performing the squint test is your “ad-scent.”
Limited Click-Fraud
Ad fraud, or “Click fraud,” is a very real problem in PPC advertising.
Ad fraud occurs when spammers, bots, and competitors click your ads.
And since you are paying “per click,” a few dozen fraudulent clicks could completely exhaust your advertising budget.

Display Advertising
Display ads most commonly consist of a picture or video and accompanying text. Most social media advertising, banner ads, Facebook, Twitter, and YouTube are all display advertising platforms.
The main difference between search ads and display ads is that display ads aim to divert a prospect’s attention away from some other internet activity like browsing Facebook. This is why display advertising is often referred to as “interruption advertising.”
If search advertising is like fishing with a net in a stream, display advertising is like fishing with a rod in the ocean: you’re dangling your bait (i.e. your ad) into a vast, diverse space and seeing what bites.

Display advertising is made difficult by the large audience size and wide variety of campaign options…
Compared to search advertising, there are more ad platforms to choose from, more placement types, and more audiences to target. There’s also far more room for marketing creativity.
Whether these differences are good or bad depends on the digital marketing agency you hire: Display ads give the pro media buyer room to “flex” their marketing chops and bring immense value to a business.
On the other hand, a display ads campaign can quickly become a financial black hole when an amateur is at the helm.
Display ads and AI
Artificial intelligence and big data have dramatically improved the viability of display advertising for narrower niches. Previously, it was only possible to use broad demographic audience targeting options like country, gender, and age.
This was fine if you were selling a product with broad appeal like women’s clothing:
You can be confident that practically everyone that views the ad either wears women’s clothing, or at least knows someone that does.
But if, for example…
You were a contractor selling luxury kitchen renovations, your ad would only be relevant to around one in five-thousand people. So display advertising wasn’t viable because most of your budget would be wasted serving up ads to people that have no interest or ability to buy what you’re selling.
This dynamic completely changed when platforms like Facebook and Twitter began using machine learning algorithms for advertising. These algorithms utilize a platform’s extensive user data to categorize users into highly specific micro-segments. When advertisers conduct a display campaign on one of these platforms, the algorithm is pre-programmed to automatically test and narrow a campaign’s audience to whatever micro-segments are predicted to be most responsive to the ad.
Pros and Cons of Display Advertising
High Volume
At the top is the campaign, where you are to indicate what your goal is for the campaign. Some common campaign goals are brand awareness, lead generation, and sales.
High Volatility
It’s not uncommon to see sudden spikes and drops in ad cost for no discernable reason.
Less Formulaic
There is a lot of variance between different types of display ads and there is far more room for creativity in a display ads campaign. For example, a Facebook feed ad allows for either images or video, and a nearly limitless volume of ad text.
Display Ad Platforms
The current undisputed king of display advertising, the Facebook ads platform also includes Whatsapp and Instagram. Facebook boasts a large and affluent audience, deep user data, and a powerful machine learning algorithm for finding niche audiences.
Facebook has generated some of the highest-ROI campaigns the internet has ever seen. For most businesses, Facebook is the correct first choice when starting off with display advertising. The main downside of Facebook is that it has very strict, unforgiving, and often ambiguous advertising guidelines.
Google Display Network
The Google display network is a large collection of online publishers that run ads in partnership with Google.
It is best known for its massive reach: an estimated 90% of the online consumer market.
The Google Display network can be a difficult place to achieve advertising success, so it’s best left until later in your advertising journey.
A great supplement to a Facebook ad campaign, it’s common for a digital marketer to port an exhausted Facebook campaign over to Twitter.
LinkedIn is a good first or second choice for B2B companies conducting a display ads campaign.
Display Ad Types
Programmatic Advertising
Publishers that want to sell off excess ad stock will join programmatic ad exchange networks that buy and sell this excess ad space at a discounted rate.
Programmatic ads require large purchase volumes and come with limited targeting options.
Native Advertising
Also known as “content recommendation,” native ads are what you see on news websites linking to other pieces of content.
Native ads can be an effective part of your content marketing strategy because they’re an effective way to build traffic to your content.
Video Ads
Video advertising brings a new dimension to display advertising. Some display ad placements, like Facebook feed ads, come with the option to use video instead of images.
Other placements, like YouTube TrueView ads, are video only. With new placement formats also comes creative new ad-cost dynamics. For example, with Youtube TrueView, advertisers are only charged when the user watches the beginning of the ad. On average, video brings higher conversion rates than images, so it’s a good idea to use video when you can.
Your Digital Advertising Campaign
Here are some of the main steps involved in conducting an online ads campaign.
1. Market Research
The goal of market research is to collect material for your ad campaign.
- Ad Creative
- Ad Copy
- Landing Pages
- Headlines
- Marketing Hooks
2 Critically Important Types of Market Research
Besides understanding the ins and outs of your business and product, there are two important types of market research to conduct.
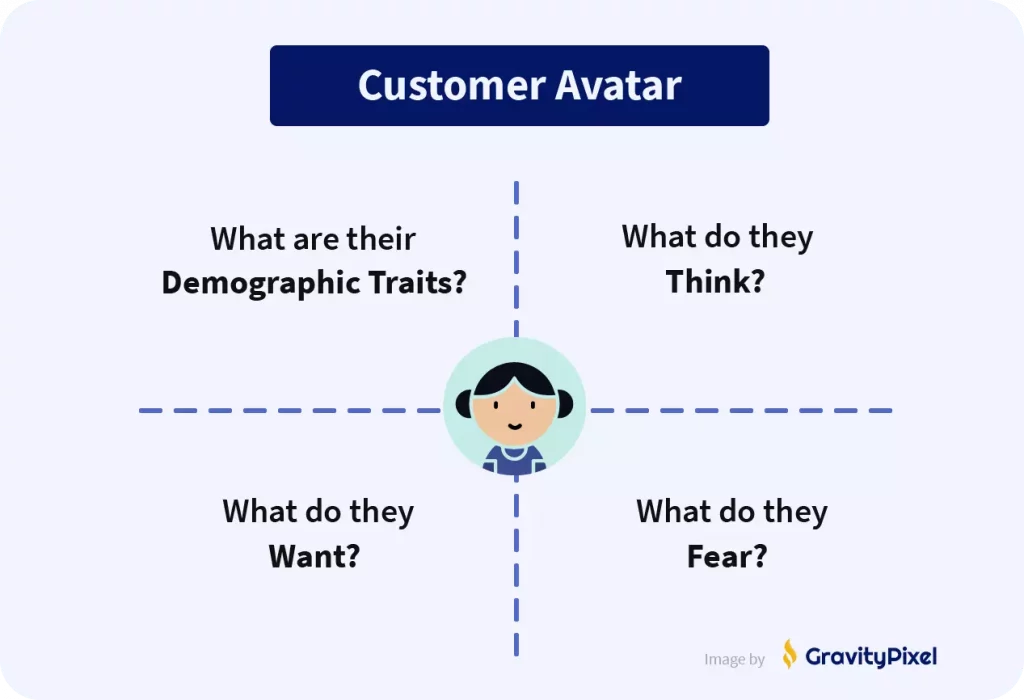
1. Avatar Research
You must extensively research your target audience. Try your best to see the world from their perspective:
Interview them, go to the forums they frequent, read what they read and watch what they watch.
- What are their demographic traits: age, gender, ethnicity, etc.
- What do they think, feel, hear, say, and do?
- What do they want?
- What do they fear?
2. Competitor Research
It’s always quite beneficial to analyze your competitors’ marketing strategies and ad campaigns. You want to get a sense for what’s working and what isn’t.
The goal is to reverse engineer successful marketing, and to discard unsuccessful strategies.
For more advanced marketers, various research tools exist that help enormously in discovering what is and isn’t working in the digital advertising world.
2. Campaign Structure
Ad campaigns generally have a 3 tier structure.
1. Campaign Level
At the top is the campaign, where you are to indicate what your goal is for the campaign.
Some common campaign goals are:
- Brand awareness
- Lead generation
- Sales
2. Ad-set Level
Below the campaign level is the “ad-set” level. Generally, here is where you select the target audience. So, if you want to test multiple audiences, you need multiple ad-sets. All these ad-sets will still be categorized under one campaign.
Your options for audience testing depend on the advertising platform you choose. The two most common audience targeting categories are demographics and interests. You can also choose among a platforms specific placements
3. Ad Level
Within each ad-set are your actual ads, which are made up of your ad-creative and ad-copy.
- Ad Creative: The goal of ad-creative is to capture your audience’s attention. Through experience, advanced digital marketers come to know the universal constants for capturing attention.
- Ad Copy: Your ad copy should continue to hook the prospect through its headline, and develop interest and desire.
3. Campaign Management
An ad campaign is a living organism that will deteriorate over time and eventually die. The purpose of campaign management is to extend the organism’s life for as long as possible.
The process of optimizing the performance of an ad campaign is known as “conversion rate optimization. The most effective way of doing this is to keep testing new marketing hooks, headlines, audiences, and creatives.
Once a campaign’s performance is optimized, you will be generating a healthy ROI. At this point, you will want to scale up your ad spending to increase the campaign’s revenue-generating power.

Start by incrementally increasing the campaign budget. As you do this, you should expect a gradual increase in conversion costs. Stop scaling before your conversion costs become undesirable.